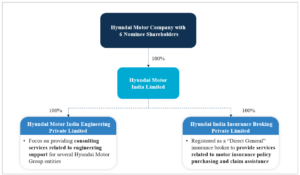
Hyundai Motor India Limited
Company
| Website 🔗 | |
| Business Activity | Manufacture |
| Division | Automobiles |
| Sub-class | Passenger Vehicles Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) and Electric Vehicles (EV) |
| Location | Sriperumbudur, Tamil Nadu Gurugram, Haryana |
| Establishment Year | 1996 |
Management
| Managing Director | Unsoo Kim |
| Educational Qualifications | Bachelor of Science (Engineering) from Seoul National University, Korea |
| Experience | Over 30 years of experience with the Hyundai Motor Group |
| Annual Salary | ₹ 18 Crores |
| Total Number of Employees | Full-time: 5,672 Off-roll : 10,171 |
About
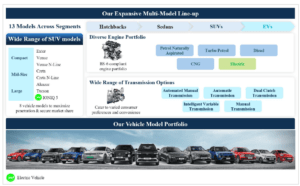
Hyundai Motor India Limited (HMIL) is a prominent player in the Indian automotive industry, renowned for its manufacturing and sale of four-wheeler passenger vehicles. The company boasts a diverse portfolio of 13 passenger vehicle models, encompassing various body types such as sedans, hatchbacks, and SUVs, including a battery electric vehicle (EV) offering. As a subsidiary of the Hyundai Motor Group, the third-largest automotive OEM worldwide, HMIL has established itself as a leader in the Indian market, holding the second-largest share in the passenger vehicle market since 2009.
Products and Services:
Hyundai Motor India Limited’s product portfolio includes a wide range of passenger vehicles, including the popular Santro, i10, i20, Creta, Verna, Exter and Venue models. The company also manufactures and sells parts, such as transmissions and engines, to companies within the Hyundai Motor Group and third parties.
In addition to its core business of vehicle manufacturing, HMIL provides various services, including after-sales services, such as warranty, insurance policy purchasing and claim assistance, financing, transportation services, and a certified pre-owned program.
Clients:
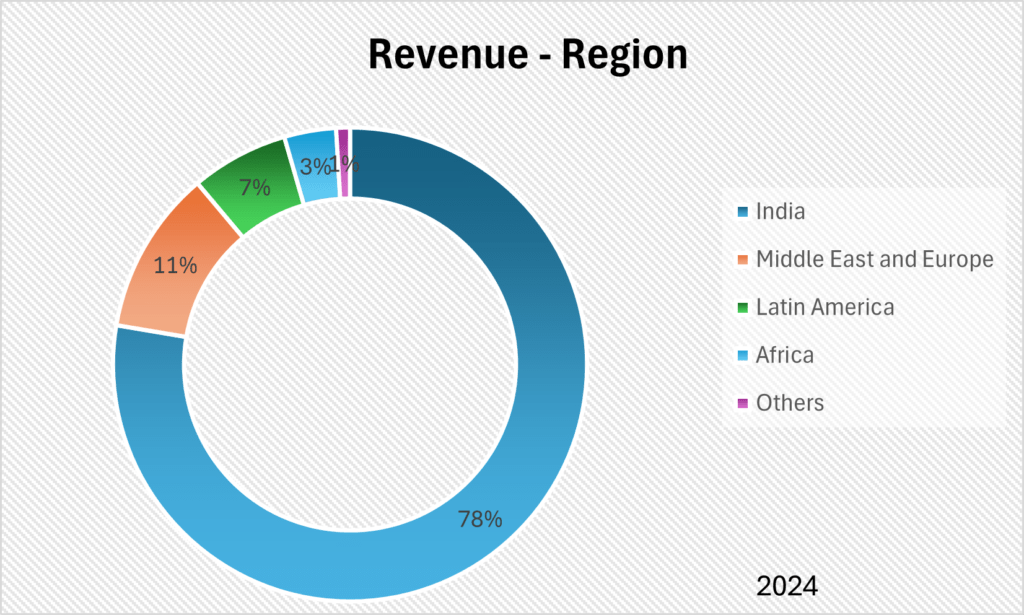
Hyundai Motor India Limited’s clientele is diverse, ranging from individual car buyers to companies within the Hyundai Motor Group. The company’s strong presence in both domestic and export markets underscores its wide customer base. HMIL has been India’s second-largest exporter of passenger vehicles since 2022, exporting to various regions, including Latin America, Africa, and the Middle East.
Manufacturing Process:
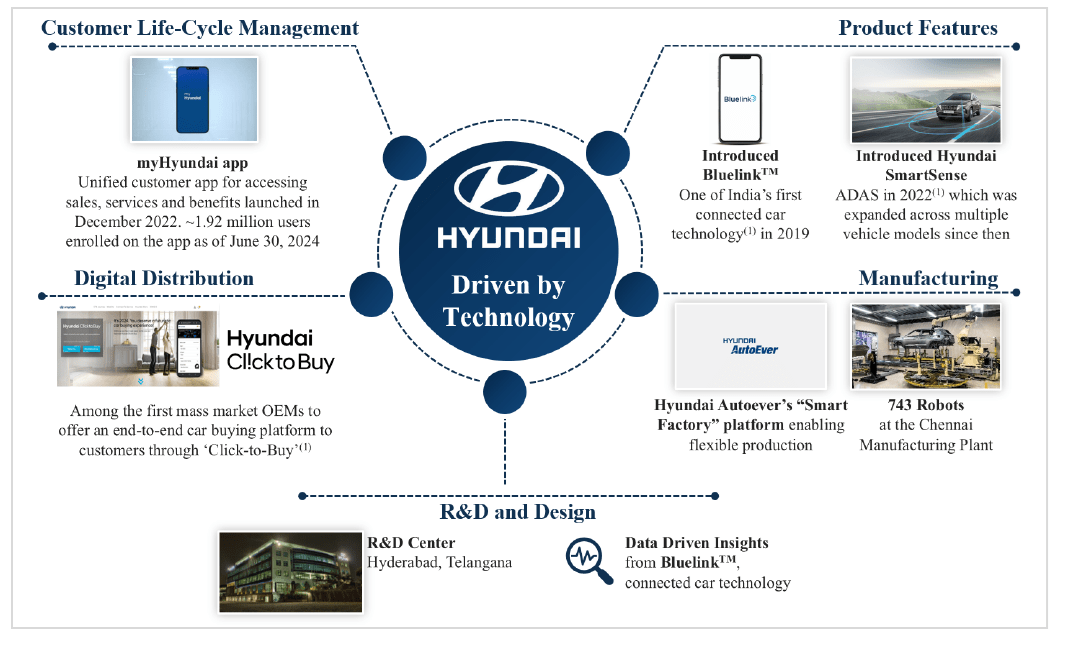
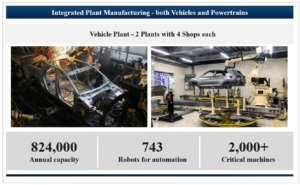
The company’s Chennai Manufacturing Plant, one of the largest single-location passenger vehicle manufacturing plants in India, is equipped with over 2,000 critical machines connected to technologically advanced systems and 743 robots. This high level of automation enables HMIL to produce a passenger vehicle every 30 seconds, highlighting the efficiency and scale of its operations.
Raw Materials:
Key raw materials include steel, aluminium, plastic, rubber, and petroleum products. The company also sources engines and transmissions from within the Hyundai Motor Group and third-party suppliers.
Suppliers:
Hyundai Motor India Limited relies on a network of suppliers for its manufacturing operations. Key suppliers include Mobis India Limited, which supplies after-sale parts and accessories, and Glovis India Private Limited, which provides transportation services. The company also sources parts and materials from other suppliers within the Hyundai Motor Group and third-party suppliers in India and overseas.
Distribution Network:
Hyundai Motor India Limited primarily sells its passenger vehicles in India through a vast network of third-party dealers. As of June 30, 2024, the company had 1,377 sales outlets across 1,036 cities and towns in India. These dealerships serve as the primary point of contact for customers, providing sales and after-sales services.
HMIL also operates one showroom in Chennai, located near its manufacturing plant, where it sells vehicles and offers after-sales services directly to customers.
In addition to its physical dealerships, HMIL has also established a digital sales platform called “Click to Buy.” This platform allows customers to browse, test drive, and purchase vehicles online, providing a convenient alternative to visiting a physical showroom.
The company also offers a mobile app, “myHyundai,” which allows customers to access various services, including booking test drives, scheduling service appointments, and accessing connected car features.
Other Key Aspects:
HMIL’s commitment to localisation is evident in its sourcing data. In Fiscal 2024 and the first quarter of Fiscal 2025, approximately 93% of the company’s parts and materials were sourced domestically. The remaining 7% was primarily imported from South Korea, mainly from Hyundai Motor Company (HMC) or other Hyundai Motor Group companies.
Research and Development:
HMIL’s R&D centre in Hyderabad plays a crucial role in this process, working closely with HMC’s centralized R&D hub in Namyang, Korea. This centre is being expanded to become the hub for global compact passenger vehicle R&D for HMC, including the proposed introduction of an automotive test tracking facility for both ICE and EV products.
Hyundai Motor India Limited exports its passenger vehicles and parts to over 150 countries. The company’s export business is primarily managed through a network of 63 international distributors.
CNG and EV:
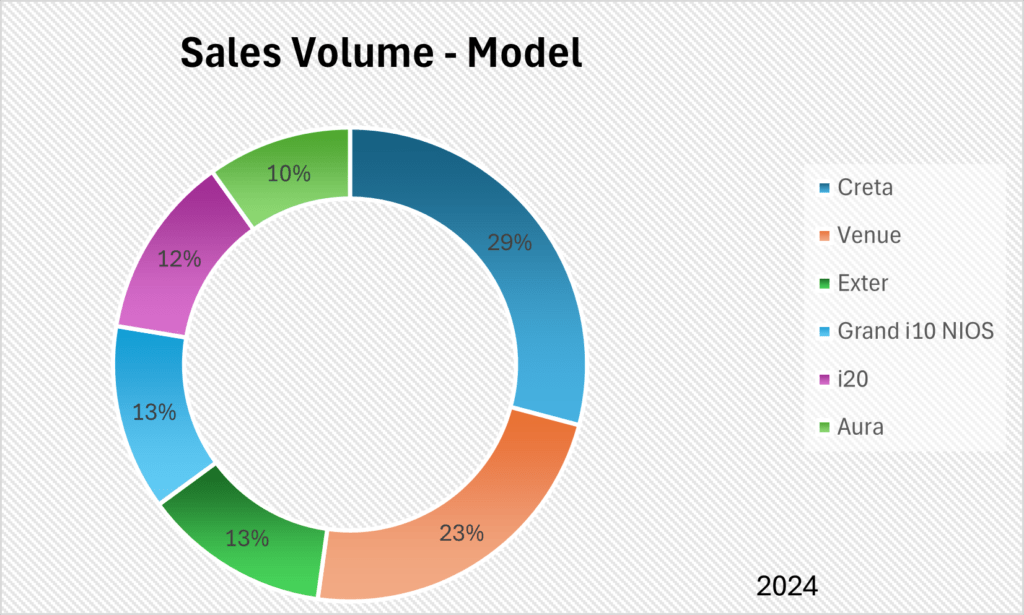
CNG and EV variants contribute about 12% of the total sales volume for FY 2024
Business Flowchart
Revenue – Category
Revenue – Region
Audit and Legal
Auditor’s Remarks:
Maintenance of Accounts:
The auditor noted that one of HMIL’s subsidiaries, Hyundai Motor India Engineering Private Limited, did not maintain daily backups of its books of account and other relevant records on servers physically located in India.
Audit Trail Feature:
The auditor noted that Hyundai Motor India Limited and two of its subsidiaries did not have the audit trail (edit log) facility enabled for their accounting software. This feature is designed to track changes made to financial data, enhancing auditability and transparency.
Non-Compliances and Other Issues:
Related Party Transactions:
HMIL engages in related party transactions with its parent company. In the three months ended June 30, 2024, expenses incurred in transactions with related parties amounted to ₹50,035.92 million, representing 32.15% of HMIL’s total expenses.
Anti-dumping duty:
In Fiscal 2015, the company paid ₹165.66 million in anti-dumping duty under protest. This was due to a provisional order imposing duties on imported cast and aluminium alloy wheels from China, Korea, and Thailand. The company has since stopped importing these goods.
Competition Act Violations:
The company faces two outstanding proceedings related to alleged anti-competitive practices. These include restrictive agreements with spare parts suppliers and exclusive supply agreements for after-sales services and spare parts with its dealers.
Contingent Liabilities:
As of June 30, 2024, the company’s contingent liabilities amounted to ₹31,461.02 million. These liabilities primarily relate to claims against the company that have not been acknowledged as debt, mainly those related to customs duty, excise duty, GST, income tax, and penalties levied by the Competition Commission of India.
Legal Cases:
Cases Filed Against the Company
Civil Litigation:
Numerous consumer cases were filed against Hyundai Motor India Limited under the Consumer Protection Act, 1982, alleging manufacturing defects in vehicles, failure to provide sale documents and delay in delivery of purchased vehicles.
Cases Filed by the Company
Tax Proceedings against the Company:
Tax Notices:
Numerous tax notices and claims related to direct and indirect taxes, including income tax, GST, VAT, service tax, and customs tax duties. Some of these claims are under dispute and are currently pending resolution.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
| Strong Market Position: The company is the second-largest automotive OEM in India, with a market share of 14.6% as of June 30, 2024. |
| Diverse Product Portfolio: The company offers a wide range of vehicles across different segments, including sedans, hatchbacks, SUVs, and EVs. |
| Strong Parentage: As a subsidiary of the Hyundai Motor Group, the company benefits from its parent’s global resources, technology, and expertise. |
| Focus on Innovation: The company has a strong track record of innovation, introducing new technologies and features to the Indian market. |
| Extensive Sales and Service Network: The company has a large network of dealerships and service centres across India, providing customers with convenient access to its products and services. |
Weaknesses
| Dependence on HMC: The company is heavily reliant on its parent company, HMC, for technology, research and development, and supply of certain critical parts. |
| Contingent Liabilities: The company has significant contingent liabilities, primarily related to tax disputes and potential penalties. |
| Legal Cases: The company is involved in several legal cases, including those related to consumer complaints, dealership disputes, and tax matters. |
Opportunities
| Growth in the Indian Automotive Market: The Indian automotive market is expected to continue to grow in the coming years, driven by rising incomes and increasing demand for personal mobility. |
| Expansion in the EV Segment: The EV market in India is expected to grow significantly, providing opportunities for the company to expand its EV offerings and market share. |
| Increasing Exports: The company has the potential to increase its exports to other emerging markets, leveraging its position as an export hub for HMC. |
Threats
| Intense Competition: The company faces intense competition from other domestic and international automotive manufacturers in India. |
| Changing Government Regulations: Changes in government regulations, including those related to safety, emissions, fuel efficiency, and taxation, could impact the company’s profitability and financial performance. |
| Economic Slowdown: A slowdown in the Indian economy could impact consumer spending and demand for passenger vehicles. |
| Rising Commodity Prices: Increases in the prices of raw materials, such as steel and aluminium, could impact the company’s production costs and profitability. |
Porter’s Five Forces1
| Threat of New Entrants | MODERATE |
| The Indian automotive market has high barriers to entry due to significant capital investment requirements, established brand identities, and complex supply chains. However, government initiatives like the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme and relaxed foreign direct investment (FDI) norms could attract new entrants, particularly in the electric vehicle (EV) segment. Hyundai’s strong market position, diverse product portfolio, and brand recognition provide a competitive edge against potential newcomers. |
| Bargaining Power of Suppliers | LOW |
| HMIL benefits from a localized supply chain, with a majority of its parts and materials sourced domestically. The company has a rigorous supplier selection process and maintains long-term relationships with its suppliers, reducing their bargaining power. The presence of a large number of suppliers in India further limits their bargaining power. However, dependence on certain suppliers within the Hyundai Motor Group, such as Mobis for after-sales parts, could increase supplier bargaining power in specific instances. |
| Bargaining Power of Buyers | MODERATE |
| Customers in the Indian automotive market have a moderate degree of bargaining power due to the availability of multiple brands and models. However, HMIL’s strong brand reputation, diverse product portfolio, and extensive sales and service network provide some leverage against buyer bargaining power. The increasing trend of premiumization and the growing demand for SUVs and EVs could further reduce buyer bargaining power in certain segments. |
| Threat of Substitute Products or Services | MODERATE |
| The threat of substitute products, such as two-wheelers and public transportation, is moderate in India. |
| Rivalry Among Existing Competitors | HIGH |
| The Indian automotive market is highly competitive, with the presence of several established domestic and international players. Competition is particularly intense in the SUV and EV segments, where HMIL is focusing its growth strategy. The industry is characterized by frequent product launches, price wars, and aggressive marketing campaigns, contributing to high competitive rivalry. HMIL’s strong market position, diverse product portfolio, and focus on innovation provide a competitive edge in this environment. |
Peer Comparison
The company’s performance on various financial and operational metrics compared to its peers for FY 2024 is as follows:
| Metric | Hyundai Motor India Limited | Maruti Suzuki India Limited | Tata Motors Limited |
| Revenue from operations (₹ million) | 698,290.57 | 1,418,582.00 | 4,379,277.70 |
| Domestic revenue (%) | 77.66 | 87.35 | 29.18 |
| Exports revenue (%) | 22.34 | 12.65 | 70.82 |
| Profit for the year margin (%) | 8.5 | 9.24 | 7.17 |
| Total sales volume | 777,876 | 2,135,323 | 1,380,315 |
| Number of sales outlets | 1,363 | 3,863 | Not available |
| Number of service outlets | 1,549 | 4,964 | Not available |
Green Box
Enhancing the Chennai Plant:
Hyundai Motor India Limited plans to develop its existing Chennai Manufacturing Plant as a hub for EV and SUV production. This involves upgrading and optimizing the current facility to increase production volume and efficiency.
Developing the Talegaon Plant:
HMIL recently acquired a manufacturing plant in Talegaon, Maharashtra. The plant is currently under redevelopment and is expected to be operational in phases, with the first phase commencing in the second half of Fiscal 2026. The Talegaon plant will further increase HMIL’s production capacity and accelerate economies of scale.
Positive Operating Cash Flow:
Hyundai Motor India Limited has maintained a positive operating cash flow in recent fiscal years.
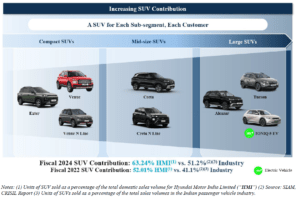
Expanding its presence in the SUV and EV segments:
Hyundai Motor India Limited has been consistently increasing its market share in the SUV segment, and the company plans to further strengthen its position in this segment by introducing new models and upgrading existing ones. HMIL is also looking to expand its presence in the EV segment, with plans to launch four new EV models in the coming years, including the Creta EV in Fiscal 2025.
Increasing its exports:
Hyundai Motor India Limited aims to leverage its local manufacturing capabilities to become an export hub for the Hyundai Motor Group, targeting emerging markets in South Asia, Latin America, Africa, and the Middle East.
Digital Media Initiatives:
HMIL leverages digital platforms, such as the “myHyundai” app and its website, to engage with customers and provide a seamless online experience for sales and after-sales services.
Customer Satisfaction Focus:
HMIL prioritizes customer satisfaction across all touchpoints, including vehicle purchase, insurance, maintenance, and after-sales services, aiming to build trust and loyalty.
Industry Outlook:
According to the CRISIL report, the Indian passenger vehicle (PV) industry is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.5% to 6.5% between fiscal years 2024 and 2029 to reach domestic vehicle sales of 5.2 to 5.7 million units by fiscal year 2029.
Amber Box
IPO Funds:
The objective of the company’s upcoming issuance of shares is to achieve the benefits of listing the Equity Shares on the Stock Exchanges and to carry out the Offer for Sale
Capacity Utilization:
The capacity utilisation rate of the company for FY 2024 is 97.1%.
Rising Inflation and Interest Rates:
The current inflationary environment and rising interest rates could impact consumer spending and make it more expensive for customers to finance vehicle purchases. This could potentially dampen demand for HMIL’s vehicles, particularly in price-sensitive segments.
Technology Disruptions:
The automotive industry is undergoing rapid technological advancements, including the development of autonomous driving, connected car technologies, and alternative fuel vehicles. HMIL needs to keep pace with these advancements and invest in new technologies to maintain its competitiveness.
Red Box
Dependence on HMC:
Hyundai Motor India Limited is heavily reliant on HMC for various aspects of its operations, including technology, research and development, and supply of certain critical parts. This dependence could potentially lead to conflicts of interest or limit HMIL’s autonomy in decision-making.
Competition from Chinese Automakers:
Chinese automakers are increasingly expanding their presence in the Indian market, offering competitively priced vehicles with advanced features. This increased competition could put pressure on HMIL’s market share and profitability.
Limited Experience in the EV Segment:
While HMIL is investing in EVs, the company has limited experience in this segment compared to some of its competitors. The success of HMIL’s EV strategy is subject to various uncertainties, including the pace of EV adoption in India, the development of charging infrastructure, and the company’s ability to compete effectively in this evolving market.
Images

- The force value of “LOW” is considered good Click Porter’s Five Forces article for more information. ↩︎
Disclaimer: The above information/document is based on publicly available sources and has been issued solely for educational and informational purposes and should not be considered as investment advice or as a Buy/Sell recommendation, or as a research report. Although due diligence has been done to ensure the accuracy of the data presented, the website or authors are not responsible for any decision arising out of an inadvertent mistake or error in the data presented on the website. The authors may also have equity shares in the companies mentioned in this report adhering to provisions of regulation 16 of the Securities and Exchange Board of India (Research Analysts) Regulations, 2014. The investor is advised to consult his/her investment advisor and undertake further due diligence before making any investment decision in the companies mentioned. Authors are not liable for any financial gains or losses due to investments made as per the information provided on this website (StocKernel.com).






